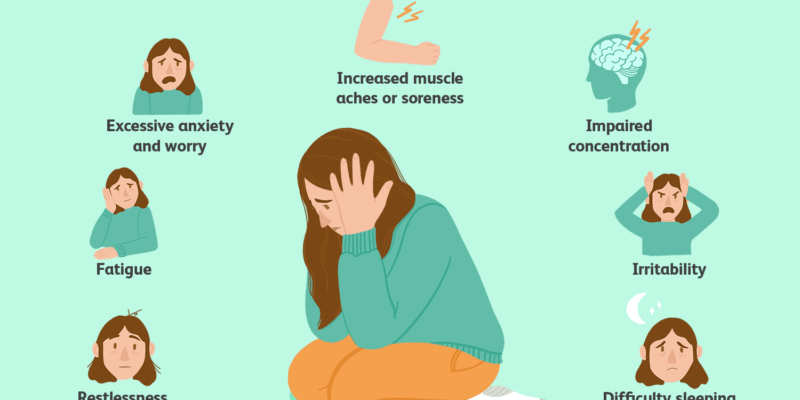
Shoulder pain can be a debilitating experience, affecting not only physical well-being but also mental health. Often, stress and anxiety exacerbate this discomfort, creating a cycle that can feel overwhelming. However, by understanding the connections between shoulder pain, stress, and anxiety, and implementing effective strategies, it’s possible to find relief and regain control of both body and mind.
Understanding the Connection
The relationship between shoulder pain, stress, and anxiety is complex and bidirectional. Stress and anxiety can manifest physically, leading to muscle tension and tightness in the shoulders. This tension can, in turn, aggravate existing shoulder pain or even cause new pain to develop. Additionally, chronic pain itself can be a significant source of stress and anxiety, creating a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion and mood. Stress and anxiety can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to gastrointestinal disturbances like gastritis. Conversely, digestive issues can also trigger stress and anxiety, creating a vicious cycle.
The Link Between Stress
anxiety are natural responses to challenging situations, but when they become chronic, they can take a toll on your physical and mental health. Persistent stress and anxiety can trigger the release of hormones that cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to a temporary increase in blood pressure. However, over time, chronic stress can also contribute to the development of low blood pressure by exhausting the body’s resources and weakening the cardiovascular system.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
- Engaging in mindfulness practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce both stress and muscle tension. These techniques promote relaxation, calming the mind and releasing physical tension in the shoulders and throughout the body.
Exercise and Stretching
- Gentle exercises and stretching routines specifically targeting the shoulders can help alleviate pain and improve flexibility. Incorporating activities like yoga, tai chi, or Pilates can be particularly beneficial as they focus on both physical movement and mindfulness, providing a holistic approach to pain management.
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
- Maintaining good posture and ergonomic practices throughout the day can prevent shoulder pain from worsening. Simple adjustments like sitting up straight, positioning computer monitors at eye level, and using ergonomic office chairs can reduce strain on the shoulders and alleviate discomfort.
Seeking Professional Help
- If shoulder pain persists despite self-care efforts, seeking professional help is essential. A healthcare provider, such as a physical therapist or chiropractor, can assess the underlying causes of the pain and develop a tailored treatment plan. Additionally, therapists or counselors can provide support for managing stress and anxiety, addressing the root causes of the physical symptoms.
Bidirectional Relationships
While stress and anxiety can lead to unhealthy eating, the reverse is also true: poor diet can exacerbate stress and anxiety. Diets high in processed foods and low in essential nutrients can contribute to poor mental health outcomes. Jacka et al. (2010) found that individuals with unhealthy dietary patterns are at higher risk for developing depression and anxiety.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Making lifestyle modifications to reduce overall stress levels can have a significant impact on shoulder pain. This may include prioritizing adequate sleep, maintaining a healthy diet, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, and establishing boundaries to prevent burnout.
Implications for Public Health
Understanding the connection between stress, anxiety, and unhealthy eating has significant public health implications. Interventions aimed at reducing stress and anxiety could potentially improve dietary habits and overall health.
ross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional research has consistently found correlations between high stress levels and poor dietary choices. For example, Torres and Newson (2007) reported that individuals with higher stress levels are more likely to consume snacks high in fats and sugars. Similarly, Oliver and Wardle (1999) found that stress is associated with increased intake of high-calorie, nutrient-poor foods
Conclusion
Managing shoulder pain in the presence of stress and anxiety requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the experience. By incorporating mindfulness practices, exercise, ergonomic adjustments, professional support, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can find relief from pain and regain a sense of control over their well-being. Remember, it’s essential to listen to your body, prioritize self-care, and seek help when needed to break the cycle of pain and stress.










