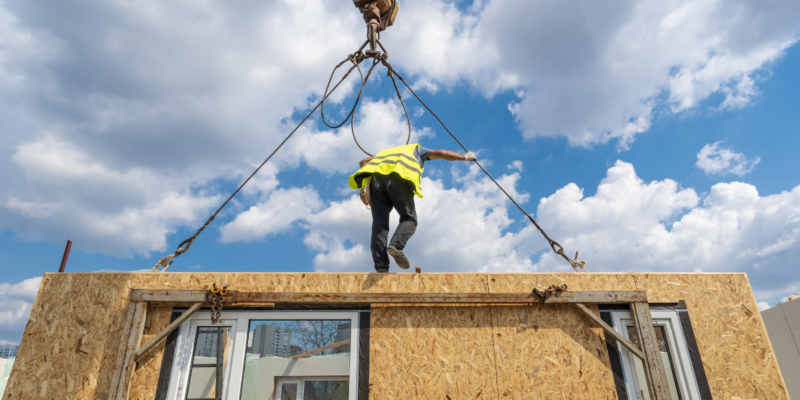
For centuries, construction has followed a familiar rhythm: hammering, sawing, and the slow rise of a structure on a dusty plot. But a revolution is brewing, with prefabricated modules taking center stage. Modular construction, a method of building where components are manufactured off-site and assembled on-site, is transforming the way we build, offering a faster, more efficient, and sustainable approach.
From Prefab to Precision: Understanding Modular Construction
Modular construction isn’t entirely new. Prefabricated structures have been around for decades, often associated with temporary housing or classrooms. However, the concept has undergone a significant evolution. Today’s modular construction involves high-quality, architecturally designed units built in controlled factory environments. These modules, ranging from bathroom pods to entire rooms or even floors, are then transported and meticulously assembled on-site.
Building a Better Way: The Advantages of Going Modular
There are many strong advantages to modular building. The following are some of the main benefits that are encouraging its adoption:
- Speed of Construction: Time is money, and modular construction saves both. When building modules alongside preparing the site, projects can be finished up to 50% quicker than when using traditional methods. This is especially helpful for projects that have short building seasons or strict deadlines.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Factory settings offer a controlled environment with consistent workflows and meticulous quality checks. This lowers the possibility of mistakes and guarantees a better caliber of construction than on-site building, which is more vulnerable to inclement weather and human error.
- Reduced Costs: While initial investment in modular construction might be slightly higher, the overall cost savings are significant. Faster completion times translate to reduced labor costs and financing fees. Additionally, less on-site waste and streamlined material management contribute to cost reduction.
- Improved Safety: Factory environments prioritize worker safety with controlled conditions and proper safety protocols. This significantly reduces the risk of accidents compared to traditional construction sites.
- Environmental Friendliness: Modular construction boasts a smaller environmental footprint. With controlled factory settings, waste generation is minimized. Additionally, the precise prefabrication reduces the need for on-site materials and transportation, minimizing the project’s carbon footprint.
- Reduced Disruption: Modular construction translates to less noise, dust, and overall disruption for surrounding communities. With most of the construction happening off-site, local businesses and residents experience minimal inconvenience.
Beyond Efficiency: Addressing the Challenges of Modular Construction
Despite its numerous advantages, modular construction faces some challenges:
- Initial Investment: Setting up modular facilities or partnering with established manufacturers might require a higher upfront investment compared to traditional methods.
- Transportation Considerations: The size and weight of modules can pose logistical challenges. Depending on the project’s location and the size of the modules, transportation costs might be a factor.
- Design Flexibility: While modular construction offers significant design freedom, there might be limitations compared to completely bespoke on-site construction. However, advancements in modular construction are constantly expanding design possibilities.
Building a Modular Future: The Road Ahead
The future of construction looks bright with modular building blocks taking center stage. As technology advances and public perception shifts, modular construction is poised for even wider adoption. Here are some exciting trends to watch:
- Standardization and Scalability: Increased standardization of modules and connections will lead to greater scalability and wider application of modular construction across different project types.
- Technological Integration: Integration of advanced technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) will further optimize design, manufacturing, and assembly of modular units.
- Sustainability Focus: As environmental concerns rise, modular construction’s inherent advantages in waste reduction and energy efficiency will become even more attractive.
Beyond the Blocks: The Expanding Horizons of Modular Construction
The core benefits of modular construction are undeniable, but its potential extends far beyond speed and efficiency. Here’s a deeper dive into how modular construction is shaping the future of various building types:
Modular Housing: The housing market is a prime candidate for disruption by modular construction. Prefabricated housing units can address the growing need for affordable, high-quality housing, particularly in urban areas. Modular construction allows for quicker turnaround times, improved quality control, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional on-site construction. This can lead to the development of more readily available and affordable housing options.
Education Revolution: Schools are constantly under pressure to expand capacity and upgrade facilities. Modular construction offers a solution for building new schools or classrooms quickly and efficiently. This minimizes disruption to ongoing education and allows schools to adapt to changing student populations. Modular building can also be used to create adaptable learning environments that meet the demands of contemporary education.
Healthcare on the Fast Track: The healthcare industry is another area where modular construction is making significant strides. Prefabricated units can be used to build new hospitals, clinics, or expand existing facilities rapidly. This is particularly beneficial in areas with limited access to healthcare or in emergency situations where quick deployment of medical facilities is crucial.
Beyond Buildings: The applications of modular construction extend beyond traditional buildings. For instance, prefabricated units can be used to create temporary housing for disaster relief efforts, or even permanent structures for refugee camps. Modular construction can also be utilized for building hotels, retail spaces, and even student dormitories.
The Rise of “Volumetric” Modules: A significant advancement in modular construction is the development of volumetric modules. These are essentially 3D sections of a building, complete with walls, floors, ceilings, plumbing, and electrical systems. Volumetric modules offer even greater speed and efficiency in on-site assembly, further streamlining the construction process.
The Future is Collaborative: The success of modular construction relies heavily on collaboration between architects, engineers, manufacturers, and logistics specialists. Integrated design and planning from the beginning of a project is crucial for a smooth transition from factory to construction site.
Building a Better Tomorrow, One Module at a Time
Modular construction is not just a new technique; it’s a paradigm shift in the construction industry. By offering speed, efficiency, sustainability, and improved quality, modular construction is well-positioned to revolutionize the way we build our homes, schools, hospitals, and cities. As we embrace this innovative approach, we can look forward to a future with faster project completion, a reduced environmental impact, and ultimately, a more long-lasting constructed environment for future generations.