Imagine a self-driving car hurtling down a freeway. Its sensors pick up on an obstruction: a car that is swerving in the other lane.
Nevertheless, it can already be too late by the time the information gets to a distant data center, which evaluates the circumstances and replies with instructions.
This scenario demonstrates why latency, or the time it takes for data to transit, is significant in today’s real-time environment.
The increasing amount of data and the emergence of real-time applications are straining these data centers’ capabilities, even if they have been of great use to us.
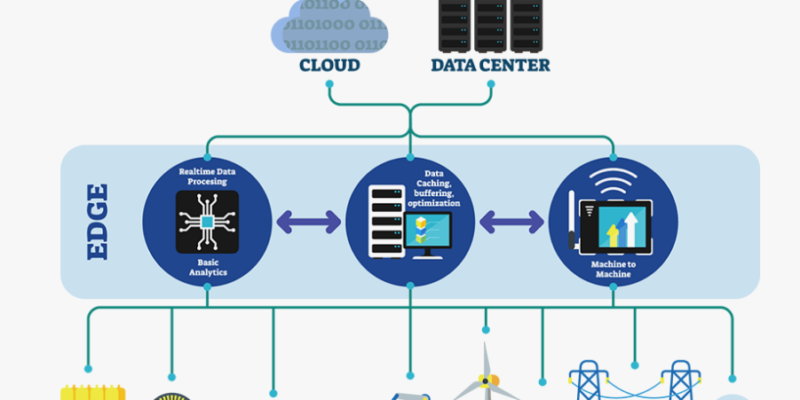
Introduced here is edge computing, a paradigm change that moves processing power closer to the edge of the network, where data originates.
This piece discusses twelve compelling reasons for edge computing as the solution to a real-time future, as well as the significance of latency.
The Power of Latency
Consider a surgeon carrying out a sensitive procedure. Real-time data, including instrument readings, augmented reality overlays, and vital signs, provides the basis for all decisions. In this case, a small delay could mean the difference between life and death.
Not only is latency an annoyance, but it can also have a big influence on user experience, safety, and performance.
The following are the various scenarios where delay appears:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Centralized processing becomes a bottleneck when billions of connected devices generate data. Real-time analysis is made possible by edge computing, allowing for efficient automation and device control.
- Autonomous vehicles: As was previously indicated, processing sensor data with a split-second latency can have disastrous consequences.
- Financial trading: To make lucrative decisions, high-frequency traders rely on almost immediate data analysis. In this hectic setting, every millisecond matters.
- Online gamers: They want things to react quickly. High latency causes lag, which can ruin an exciting win and make it feel like a painful loss.
- The user and the virtual world must seamlessly interact for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to function. Latency disrupts this flow and causes dizziness and nausea.
Essentially, latency poses a threat to real-time systems. The delay increases with the distance that data must travel. This is where edge computing comes into play, providing a means of bridging the data-generating and processing divide.
Reasons for Edge Computing as the Solution
Edge computing increases the network’s reach by bringing processing power closer to the data generation point. With so many advantages, this distributed strategy is the preferred choice for a real-time future. These are a dozen strong arguments for why:
1. Better Experience for Users
A smooth user experience is largely dependent on low latency. For example, consider applications utilizing augmented reality. Jittery graphics and a disturbed user experience can result from data processing delays. By handling data locally and reducing latency, edge computing makes sure that augmented reality experiences run smoothly.
2. Enhanced Reliability
Data centers that are centralized are vulnerable to interruptions and outages in the network. Edge computing offers a more distributed architecture where local processing continues even if the connection to the central hub is lost. Increased dependability and continuous operations are the results of this redundancy.
3. Lessened Bandwidth Consumption
With edge computing, the data center just needs to receive the most important data. This leads to a large reduction in bandwidth use, which is especially advantageous for locations with low bandwidth, such as rural areas, or devices with restricted resources.
4. Enhanced Security
To abide by data privacy laws, sensitive data must frequently be processed locally. By enabling on-device or on-premises data processing, edge computing reduces the possibility of illegal access and data breaches.
5. Optimized Cost Efficiency
Data transmission expenses can be reduced with the use of edge computing. Businesses can save a lot of money on their IT infrastructure by lowering their dependency on data centers and using less bandwidth.
6. Simplified Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
As IoT devices proliferate, enormous volumes of data are produced. The IoT landscape may expand more easily with the help of edge computing, which provides a scalable way to handle this data and enable real-time insights from connected devices.
7. Better Smart City Operations
Real-time data is essential to smart cities’ garbage collection, traffic control, and environmental monitoring systems. Edge computing makes it possible to process data locally and respond more quickly, which improves city operations and supports smart city efforts.
8. Revolutionized Healthcare
The healthcare industry has a lot of opportunities for edge computing. Wearables and medical devices can use real-time data processing to achieve remote patient monitoring. This can help with faster interventions and better patient outcomes.
9. Speedier Making of Decisions
Every millisecond matters when there is pressure to hurry. Without having to communicate back and forth with a faraway data center, edge computing enables on-the-spot data analysis. In applications like driverless vehicles, industrial automation, and stock trading, this equates to faster insights and faster decision-making.
10. Increased Operational Efficiency
Manufacturing facilities can use edge computing to implement predictive maintenance plans, optimize production lines, and identify equipment issues in real-time. Reduced downtime and increased operational efficiency result from this.
11. Using AI to Its Full Potential
Edge computing can help with on-device or on-premises AI processing. This facilitates quicker AI deployment and training, which is especially helpful for real-time anomaly detection and facial recognition applications.
12. The Advent of 5G
This technology promises extremely fast speeds and little latency. Technology is developing at a faster rate than before because edge computing and 5G together will open up a new world of real-time services and applications.
The End of the Future Is Near
Data processing has undergone a fundamental change with the emergence of edge computing. Edge computing enables a new generation of real-time services and applications by putting speed and efficiency first.
It promises speedier decision-making, improved user experiences, and unmatched efficiency as we transition to a more connected and data-driven society.
There is no doubt that edge computing will grow as we progress toward a more data-driven and networked society.










