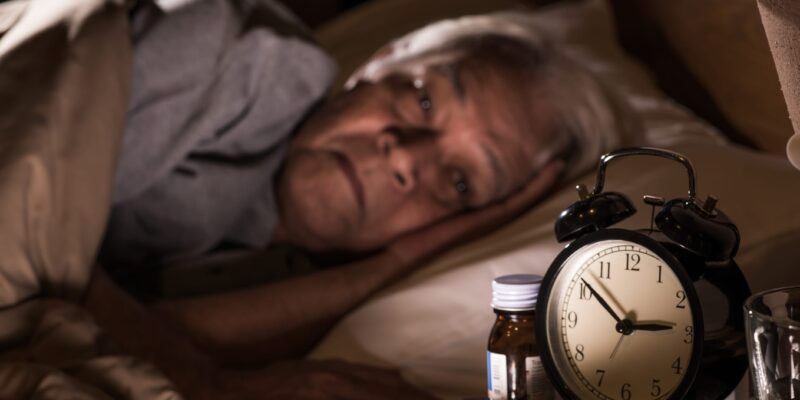
Insomnia, a prevalent sleep disorder affecting millions worldwide, manifests as difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and struggling to resume sleep. While causes vary from stress and lifestyle factors to medical conditions, recent research has delved into the intriguing link between gut health and sleep quality. Probiotics, known for their beneficial effects on gut microbiota, have emerged as a potential non-pharmacological intervention in managing insomnia.
Understanding Insomnia and its Impact
Insomnia disrupts the natural sleep-wake cycle, leaving individuals fatigued, irritable, and unable to function optimally during waking hours. Chronic insomnia increases the risk of developing mental health issues like depression and anxiety, compromises immune function, and contributes to cardiovascular problems. Traditional treatments often involve medications that may lead to dependency or unwanted side effects, underscoring the need for alternative approaches like probiotics.
The Gut-Brain Axis: Exploring the Connection
The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system, plays a crucial role in regulating sleep patterns. The gut microbiota, composed of trillions of microorganisms, influences this axis by producing neurotransmitters, hormones, and metabolites that affect brain function, including sleep regulation.
Probiotics: Nature’s Sleep Regulators?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and yeasts, that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They populate the gut microbiota, promoting a balanced microbial environment associated with various health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and potentially, better sleep quality.
Mechanisms of Action
- Neurotransmitter Production: Certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Serotonin regulates mood and sleep, while GABA inhibits neuronal activity, promoting relaxation and sleep onset.
- Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation disrupts sleep patterns. Probiotics help modulate inflammation by enhancing gut barrier function and reducing systemic inflammation, potentially improving sleep quality.
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Probiotics influence the production of metabolites that regulate circadian rhythms, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs derived from dietary fiber fermentation contribute to maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
Clinical Evidence and Studies
Research exploring probiotics’ impact on sleep quality remains in its infancy but shows promising results:
- A study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry indicated that individuals consuming a probiotic-containing yogurt experienced improvements in sleep quality and duration compared to those consuming a placebo.
- Another study in Nutrients found that supplementation with certain probiotic strains reduced insomnia symptoms in participants with sleep disorders.
While these studies are preliminary, they highlight probiotics’ potential as a safe and natural approach to complement traditional insomnia treatments.
Choosing the Right Probiotic
Selecting an effective probiotic for improving sleep requires consideration of several factors:
- Strain Specificity: Different probiotic strains may have varying effects on sleep. Look for strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum, which have shown promise in promoting relaxation and sleep quality.
- Dosage and Formulation: Opt for products with clinically validated dosages of probiotics and ensure they are formulated to survive stomach acidity and reach the intestines alive.
- Combination Therapies: Combining probiotics with prebiotics (fiber-rich foods that promote probiotic growth) and a healthy diet can enhance their effectiveness in improving sleep.
Integrating Probiotics into Your Routine
If considering probiotics to manage insomnia, consult a healthcare provider to determine suitability, especially if managing underlying health conditions. Probiotics are generally safe for most individuals, but potential interactions with medications or existing health conditions should be evaluated.
Lifestyle Considerations
While probiotics show promise in managing insomnia, integrating them with healthy sleep hygiene practices maximizes their benefits:
- Sleep Environment: Create a conducive sleep environment by minimizing noise and light, optimizing room temperature, and using comfortable bedding.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to alleviate stress and promote better sleep.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Maintain a regular sleep-wake cycle, even on weekends, to reinforce circadian rhythms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while more research is needed to fully elucidate probiotics’ role in managing insomnia, emerging evidence suggests they may offer a valuable adjunctive therapy. By supporting gut health and influencing the gut-brain axis, probiotics show promise in improving sleep quality naturally and without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical interventions. As interest in integrative health grows, probiotics represent a novel frontier in the quest for effective, holistic approaches to managing sleep disorders like insomnia.