Testicular health is a topic that often goes under the radar for many men, yet it is crucial for overall well-being. One common issue that can cause discomfort and concern is swollen testicular veins. This condition, known medically as varicocele, can lead to pain, infertility, and other complications if not properly addressed. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for swollen testicular veins, ensuring you have all the information you need to manage this condition effectively.
What are Swollen Testicular Veins?
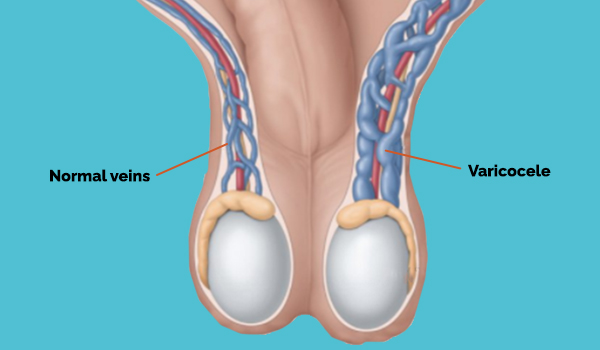
Swollen testicular veins, or varicocele, occur when the veins within the scrotum become enlarged and dilated. This condition is similar to varicose veins that appear in the legs. The veins within the scrotum called the pampiniform plexus, are responsible for draining blood from the testes. When these veins become enlarged, blood flow can be impaired, leading to various symptoms and potential complications.
Causes of Swollen Testicular Veins
Understanding the causes of swollen testicular veins is essential for prevention and treatment. Several factors can contribute to the development of a varicocele:
Genetics: A family history of varicoceles can increase your risk.
Anatomical Factors: Structural differences in the veins and valves in the scrotum can lead to varicocele.
Increased Pressure: Activities or conditions that increase pressure in the abdominal area, such as heavy lifting or chronic constipation, can contribute to the development of varicocele.
Symptoms of Swollen Testicular Veins
Varicocele may not always present noticeable symptoms, but when it does, they can include:
- Aching Pain: A dull, aching pain in the scrotum, which may worsen after physical activity or prolonged standing.
- Swelling: Visible or palpable enlargement of the veins within the scrotum.
- Infertility: Reduced sperm quality and quantity, leading to fertility issues.
- Testicular Atrophy: Shrinking of the affected testicle.
Diagnosing Varicocele
If you suspect you have a varicocele, it’s important to seek medical advice. Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will examine the scrotum while you are standing and lying down to detect enlarged veins.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound can provide a detailed image of the scrotum and help confirm the presence of varicocele.
Treatment Options for Swollen Testicular Veins
Treatment for varicocele depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on fertility. Options include:
Watchful Waiting
For mild cases without significant symptoms or fertility issues, a “wait and see” approach may be recommended. Regular check-ups ensure the condition does not worsen.
Medication
While there is no specific medication to treat varicocele, pain relief can be managed with over-the-counter painkillers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Surgical Options
Surgery may be necessary for more severe cases or when fertility is affected. Surgical options include:
Varicocelectomy
This is the most common surgical procedure for varicocele. It involves tying off the affected veins to redirect blood flow to normal veins. It can be performed through open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or microsurgery.
Embolization
A less invasive option, embolization involves inserting a catheter into the groin or neck to block the affected veins. This procedure is done under local anaesthesia and has a shorter recovery time compared to surgery.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, certain home remedies and lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of varicocele:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity to improve blood circulation.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Minimize activities that increase abdominal pressure.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet high in fiber can prevent constipation, reducing strain on the abdominal veins.
- Wear Supportive Underwear: A jockstrap or supportive underwear can help alleviate discomfort.
The Role of Nutrition in Testicular Health
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining testicular health and managing varicocele. Some key nutrients include:
Zinc: Essential for sperm production and overall testicular health. Found in foods like nuts, seeds, and seafood.
Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E can help protect testicular tissue from damage. Found in fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Support blood flow and reduce inflammation. Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Complications Associated with Untreated Varicocele
Ignoring a varicocele can lead to several complications, including:
Infertility: Prolonged varicocele can significantly impact sperm quality and quantity.
Testicular Atrophy: Persistent varicocele can cause the affected testicle to shrink.
Chronic Pain: Ongoing discomfort and pain in the scrotum.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience:
Persistent pain or discomfort in the scrotum.
Noticeable swelling or enlargement of the veins in the scrotum.
Difficulty with fertility or trying to conceive for an extended period.
Preventing Swollen Testicular Veins
While not all cases of varicocele can be prevented, certain measures can reduce your risk:
Regular Check-ups: Routine medical examinations can detect early signs of varicocele.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid activities that increase abdominal pressure.
Proper Hydration: Stay hydrated to support overall blood flow and vascular health.
Conclusion
Swollen testicular veins, or varicocele, is a common condition that can affect men of all ages. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices and seeking timely medical advice, you can mitigate the impact of varicocele on your health and well-being. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to preventing complications and ensuring optimal testicular health. If you suspect you have a varicocele, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.











